I'm a big user of Chrome devtools, and it's a core part of my web dev workflow. I've also started looking at service worker support and 'add to home screen' in some of my projects and there's a few bits that I need to test directly on the device.
My only tiny problem is: I have a USB3 based phone (a OnePlus 2). I have oodles of USB2 cables, but only a single USB3 cable. So I figured out how to remote debug over wifi instead.
Note that this post is for Chrome for Android, and much more focused towards to Oxygen based OSs.

MY EBOOK£5 for Working the Command Line
Gain command-line shortcuts and processing techniques, install new tools and diagnose problems, and fully customize your terminal for a better, more powerful workflow.
£5 to own it today
When I started this post, it was supposed to be a short, sweet and to the point. Except then I realised there were a few prerequisites that some people might not know, so I've now split this post into the short version and the longer, don't assume anything version.
The short version
If you're not running vanilla Android (like Cyanogen or Oxygen) you might also have a menu item called "ADB over network": enable this.
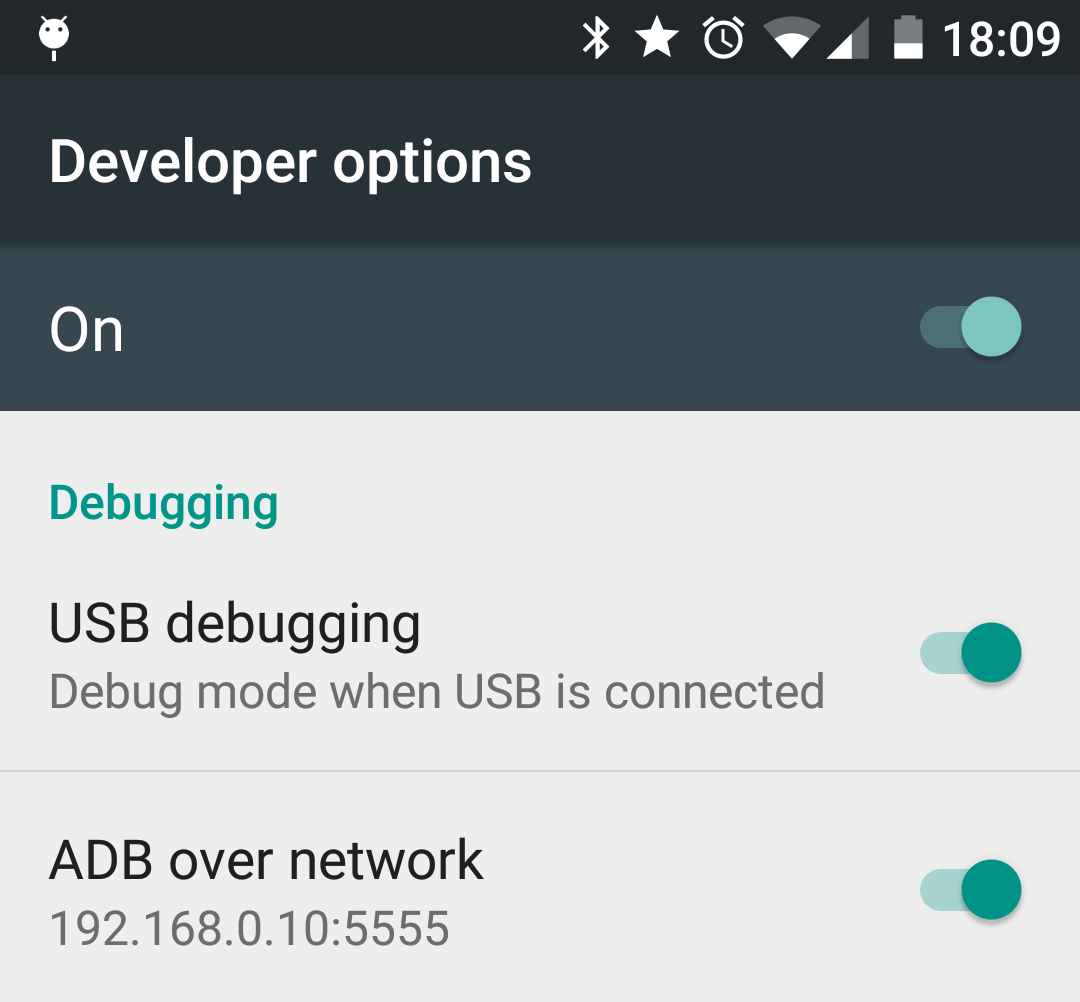
Then from your terminal, you'll need to connect to the IP that ADB over network shows:
$ adb connect <IP>:5555
If you don't have ADB over network, you can switch ADB to use TCP, but it requires a one time USB connection. Once you've connected up your Android run the following BASH commands in your terminal:
$ ID=$(adb devices | \
awk -F'device' '{if (match($0, /device$/)) print $1}');
$ IP=$(adb shell ifconfig wlan0 | \
awk '{if (sub(/inet addr:/,"")) print $1 }');
$ adb tcpip 5555;
$ adb connect $IP:5555
Now you device is connected over the network, you can remote debug.
Remote debugging without USB
Now that you've removed your USB cable, you can head to chrome://inspect and you should see your device (if not, either try refreshing or running adb devices, it should soon enough):
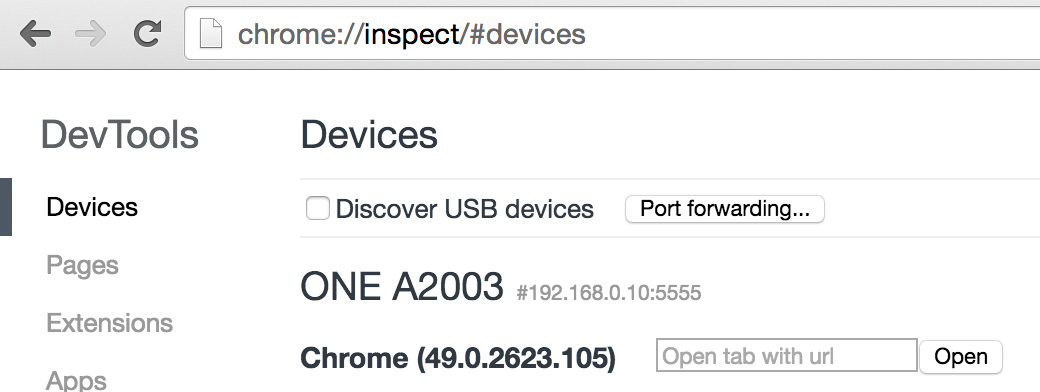
Now, even though the "Port forward" is under the "Discover USB devices" this actually works over TCP too. So you can enable forwarding localhost to your machine for testing things like service workers since they have a whitelist for localhost.
That's it, but please also read the final note about security.
The long version
I'm expecting that your device is on the same network as your machine you want to remote debug from (I'm sure it's possibly otherwise, but I've not personally tested this boundary). You will also need the developer options enabled:
- Settings
- About phone
- Tap "Build number" 7 times to enable the Developer Options (which appears in Settings).
From developer options enable "USB debugging". If you're not running vanilla Android (like Cyanogen or Oxygen) you might also have a menu item called "ADB over network": enable this.

If you've got ADB over network, you can skip to remote wifi debugging. If not, you've got a few more hoops to jump through.
Vanilla Android
If you don't have ADB over network, then you've got two options:
- Root your device (which I can't advise on)
- Manually switch on ADB over network
If you have a rooted device, then download and install an ADB over wifi app from the Play Store. This will let you effectively enable the same ADB over network option you saw above. You can now skip to remote wifi debugging.
If you don't have a rooted device (like me), the only way you can use ADB over wifi is to enable it first using a USB connection.
Enabling ADB over wifi
To achieve this, you need to active ADB using your USB connection. This is required each time you want to start a new ADB session. Firstly, connect your device using USB to your machine.
Next, you need to run adb. If you've never done this before, then you'll need to install adb (Android Debug Bridge) but for that I'll refer you to this article.
Now we're going to do the following using adb:
- List the connected devices
- Get the local IP address of our device
- Restart ADB in TCP mode
- Reconnect ADB manually
The follow BASH script does all those steps for you. So you can copy and paste the commands (if you're on a mac or linux), and drop it directly in your terminal application:
$ ID=$(adb devices | awk -F'device' '{if (match($0, /device$/)) print $1}');
$ IP=$(adb shell ifconfig wlan0 | awk '{if (sub(/inet addr:/,"")) print $1 }');
$ adb tcpip 5555;
$ adb connect $IP:5555
Now, disconnect the USB cable. You can validate it worked by running adb devices and it should now list the IP of the device.
Connecting
Before remote debugging, you need to connect to your device using adb (note if you don't have it, again, use this link).
You need to know the IP of your device, which you should be able to discover using one of the discovery techniques I've covered above. Next, we connect:
$ adb connect <DEVICE_IP>:5555
connected to <DEVICE_IP>:5555
Now you're ready for remote debugging without USB.
Final note about security
Whilst your device is running in ADB over network mode, it's open for anyone to connect to your device. It's recommended that you use this method over a trusted network, and most importantly, turn off the ADB over network once you're finished.
If you manually switched ADB to use the network (using the vanilla method), then disconnecting (using adb usb to return to USB mode) should reset the state.